
Updates

Status Inspections Programme
30 Jun 2023The RSC inspection programme consists of Structural, Electrical, Fire, and Boiler safety inspections. This section of the report represents the total number of inspections conducted by RSC since its inception . The RSC carried out 17,220 inspections from June 2020 to May 2024 (among a total of 63,047 inspections by the safety initiative since 2014).
- RSC engineers conducted 1,700 (covered and non-covered factory) initial inspections in the RSC period among the total of 8,096 initial inspections.
- RSC engineers conducted 15,520 follow-ups and other safety inspections in the RSC period, among the 54,951 follow-up and other safety inspections.
Following the initial inspections, the factory and the brands are tasked to develop a Corrective Action Plan (CAP) that details the time-bound remedial action(s) for completion which is based on the severity of the findings. RSC regularly coordinates with the factories to ensure that the outstanding CAPs are being completed and conducts follow-up inspections to monitor that the remediation processes are duly implemented. Other safety inspections include post-incident inspections, OSH complaints initial inspections, fire safety inspections, OSH complaints verification inspections, unannounced OSH complaint inspections, and inspections based on the Safety Committee Walk Through. Factories are now being inspected within 4 – 5 months’ interval which was 8 months before.
FACTORY COVERAGE (As of May 2024)
- Covered factory account number: 1779
- 26 new “Independent factories” were listed through the industry (BGMEA, BKMEA) for participating in the RSC's inspection and remediation programme.
- As of May 2024, 51 factories were waiting for initial inspection.
Since 74 no-brand factories were archived in May 2024, the total number of covered factories decreased from April 2024.
The following graph shows the total factories being covered by RSC from September 2023 to May 2024.
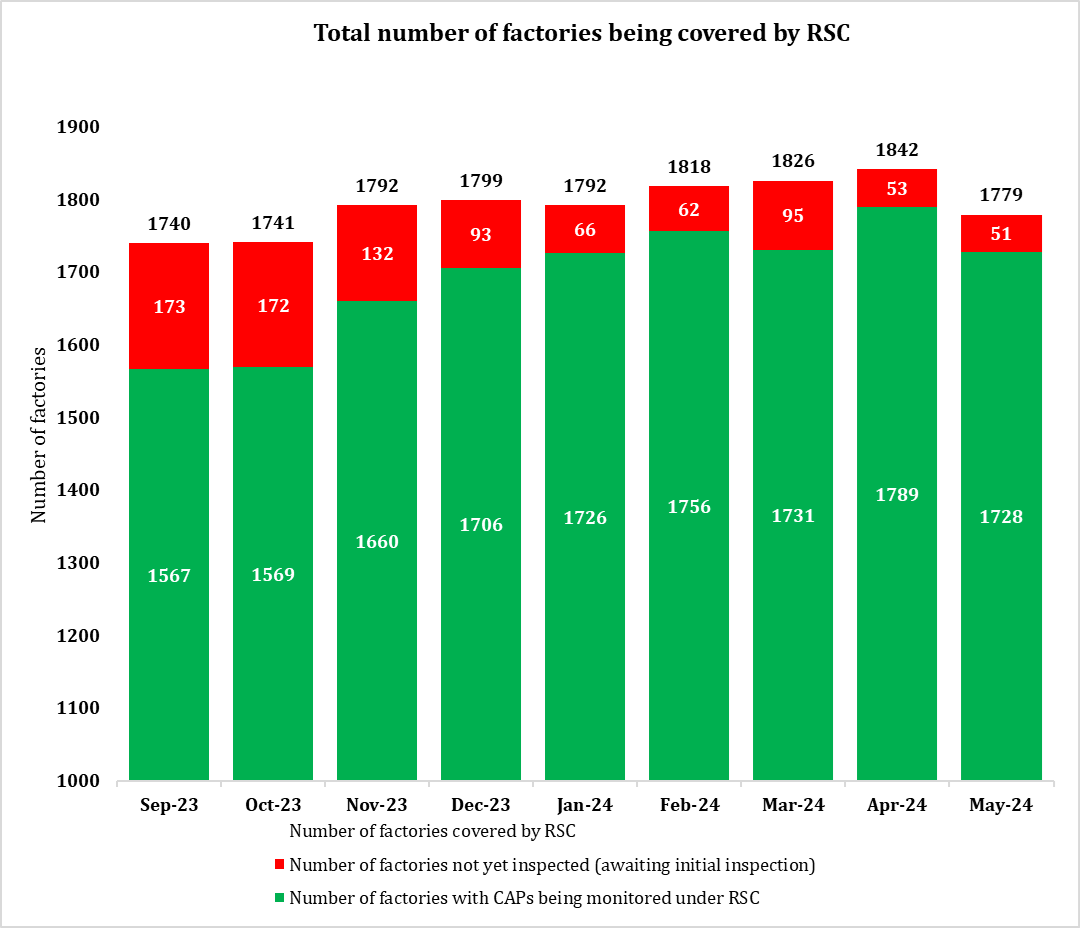
Figure 1: Number of factories covered by RSC
INSPECTIONS HIGHLIGHTS
- Total number of inspections: 642 in May.
- Number of unique factories inspected: 509 in May.
- The total inspection number is 1.26 more than the number of unique factories covered, indicating multiple inspections conducted simultaneously.
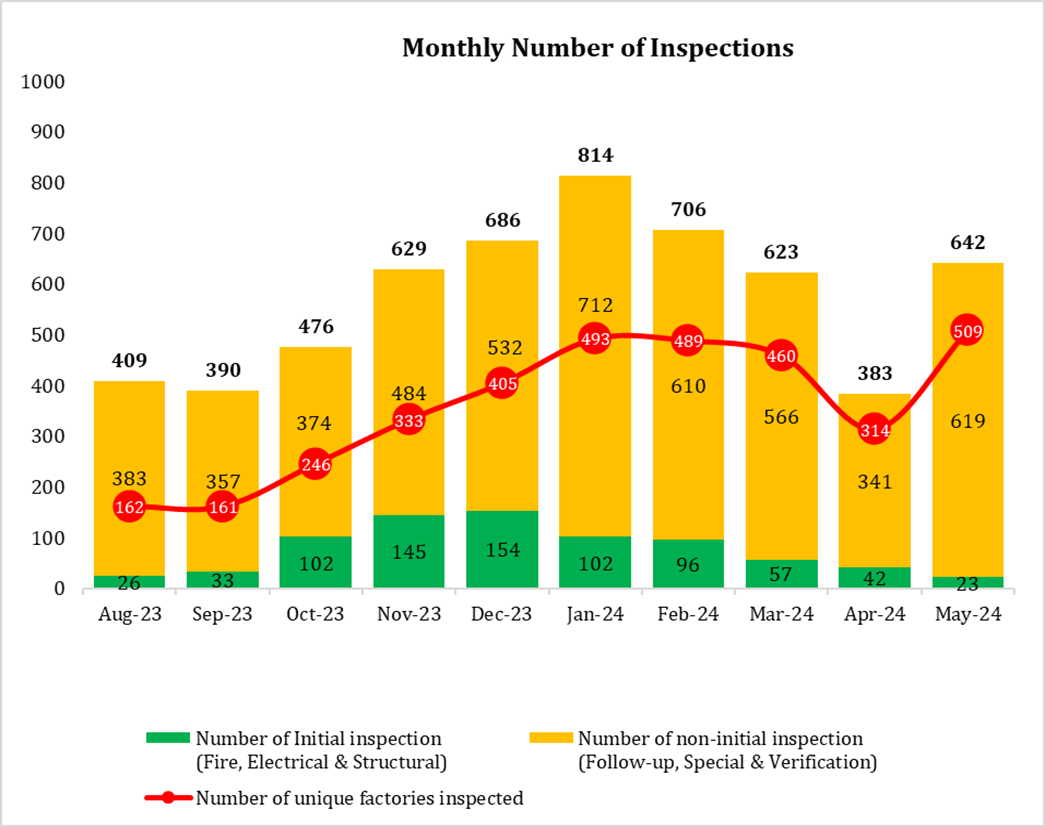
Figure 2: Number of Inspection conducted by the RSC
Recent Posts






